Best Practices for Loading and Firing Your Skutt Kiln
Skutt electric kilns are designed with the goal of having uniform heat throughout the entire kiln chamber. This is primarily accomplished through the use of balanced elements installed at the top and bottom of the kilns to help compensate for the natural heat loss that occurs through the lid and floor of a kiln. The center of the electric kiln is typically the hottest area simply because of a higher concentration of elements. By putting elements that get slightly hotter at the top and bottom of the kiln and elements that don’t fire as hot in the center of the kiln, the heat is more evenly distributed throughout the entire chamber.
Balanced elements do a good job of evening out the heat throughout a kiln, especially taller models like the 1027 and 1227, but other factors can influence distribution of heat and cone bends throughout the chamber including:
• Separation of kiln shelf layers
• Thermocouple placement
• Evenness of kiln load
• Density of load
• Shelf size
• Firing speed/heating rates
• Hold time
• Use of an EnviroVent 2 downdraft system
• Cone type
• Cone placement
Separation of Kiln Shelf Layers and Thermocouple Placement
There are many reasons that a kiln can fire unevenly. Barring a mechanical problem like an element or relay not functioning, the most common issue we encounter is poorly loaded kilns with shelves stacked too tightly together.
Separation of kiln shelf layers can have a dramatic effect on fired results. The tighter the shelf layers, the more challenging it is for radiant heat from the elements to penetrate evenly between the layers. This is especially true at the top and bottom of the kiln where a more significant amount of heat is lost through the lid and floor slabs. Balanced elements help, but they can only do so much to compensate.
Recommended loading patterns include placing a one-inch post on the kiln floor, then the first kiln shelf, followed by a 5-6-inch-tall kiln post and then the second shelf layer, etc. Using a taller kiln post between the first and second layer in the bottom of the kiln effectively exposes that layer to two full rows of element coils in the side walls. This typically gives the best ability for more uniform heat in that area.
The same theory holds true at the top of the kiln. The uppermost shelf should be placed no closer than approximately 5 inches from the underside of the lid, such that two full rows of element coils are visible to radiate heat onto that shelf layer. Shelves stacked tighter at the top and bottom of the kiln have a greater likelihood of being underfired. While each kiln is different and some clay and glazes are more forgiving than others, if consistency and uniformity of heat is required, then the shelves at the top and bottom of the kiln need to be exposed to more radiant heat.
The shelves in the center of the kiln can generally be stacked somewhat tighter because it is naturally hotter in that area. Two-inch posts can potentially be used for flat objects, but often three inch or taller posts are better for low objects. The exception to this is the shelf layer near the thermocouple in the middle of the kiln. Skutt recommends an ideal clearance of two inches all around the tip of the thermocouple so that it can measure temperature unobstructed. Kiln shelves, posts, or pottery placed very close to the tip of the thermocouple can interfere with its ability to measure air temperatures accurately.
Density and Evenness of Kiln Load
Evenness of kiln load and density of load can also impact fired results. Tall kilns that are loaded very unevenly will not fire uniformly. Four shelf layers in a 27-inch-tall kiln is average. If six-inch posts were used between each of the four layers, the load would be very evenly distributed and the kiln should fire quite evenly. However, as an extreme example, if all four layers were stacked with plates at the bottom of the kiln using two-inch posts between the layers and the uppermost shelf was wide open to the lid, the kiln would not fire accurately and the plates on the lower shelves would be underfired because the heat could not radiate in between the very tight layers.
Kilns can be successfully fired partially full if needed. For instance, if there is enough work to fill approximately 40% or more of the kiln, the items should be spread out to make use of the entire kiln chamber, rather than being concentrated at the bottom of the kiln. If there is less than 40%, or approximately 1/3 of a full kiln load, then the shelves should be propped up and the pieces placed on one or two shelf layers in the center of the kiln. Taller kiln posts (approximately six inches) should be used to separate the shelves in this case to let the kiln to be as open as possible between those layers and to allow ample room around the thermocouple.
Kiln Shelf Size
Selection of kiln shelf size in relation to chamber size is also important. Shelves that are too wide for the chamber can restrict heat flow throughout the kiln. Ideally, there should be approximately one-inch or more of clearance between the edge of the kiln shelf and the wall of the kiln chamber. Shelves that extend too close to the kiln wall can effectively cut off the ability of heat to move more easily throughout the kiln chamber.
Firing Speed
The choice of firing speed should be made according to the scale of work and cone temperature being fired to. The kiln should be fired according to the needs of the weakest link inside, which is the biggest, thickest, or wettest item in the firing.
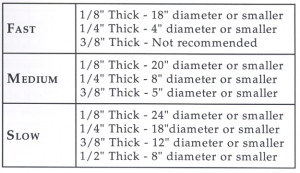
Preset modes include Slow, Medium, and Fast. Fast is primarily designed for China paints, lusters, overglazes, and decals – firings that go to relatively low temperatures and can be done quickly. Fast mode can occasionally be used successfully for some higher temperature glaze firings, but it is often not recommended because it is typically too fast for most clay and glazes to mature properly. It is not recommended for most bisque firings. More often the choice should be limited to Slow or Medium. The selection is decided based on how physically thick or large is the work in the kiln. As a general rule, the larger or thicker the item, the slower it should be fired.
Work that is similar in thickness to that of a pencil (3/8” or less) is generally considered “average” thickness and can be safely fired on Medium speed. The exception to this would be for very large objects. Items approximately 15-18 inches or more in any dimension or pieces that nearly fill the full width or height of the kiln should be fired on Slow so that the entirety of the piece can heat up more uniformly.
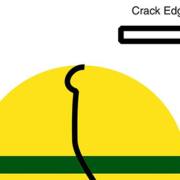
Items that are approximately 1/2-inch thick should be fired on Slow. These would be considered “thick” and need to be fired more slowly so that the exterior of the clay does not get substantially hotter than the interior. A significant temperature differential on the same piece, because of thickness or extreme size, can lead to stress in the clay which promotes cracking. Items that are more than approximately ¾-1-inch thick or greater may need to be fired using a custom program that slows the entire program down even more to accommodate for the extra thickness.
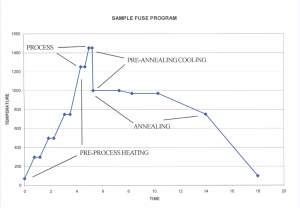
Heating and Cooling Rates
The programmed heating rate in the final segment of the firing is what primarily impacts the heat work attained in the kiln. Heat work is the measurement of time and temperature together. The faster something is fired, the hotter the peak temperature needs to be. The slower it goes, the lower the temp can be. Fast mode is programmed to heat at a rate of 200 °F per hour in the final 250 °F of the program. For comparison, the Medium speed mode is programmed at 120 °F per hour and Slow is at 80 °F per hour. Orton calibrates their cones to a rate of 108 °F per hour in the final segment.
Because heat work is achieved during the final segment, cooling rates, unless programmed to be exceptionally slow, do not typically impact cone bend results in electric kilns the way they might in a gas kiln with substantially thicker walls and more mass that continues to radiate heat after the firing has completed. Electric kilns typically drop rapidly in temperature very quickly after the power is shut off to the elements. The rate is quick enough that 200 °F can easily be lost in the first 20 minutes following completion of a firing. Once the kiln has cooled that much, heat work is no longer a factor for the clay and glaze maturity.
Hold Time
A short hold time of 5-15 minutes at the peak temperature is a simple method of helping to even out heat work throughout a kiln chamber. For example, if one section of the kiln is a half cone cooler than the rest of the kiln, a 10-minute hold at the peak temperature may be all that is needed to even out the heat work in the kiln. Because the middle of the kiln tends to be the hottest area, the hold time will tend to fire the middle of the kiln slightly hotter. For clay and glazes that appear to be underfired when the target cone is partially bent, this is a good indication that they can handle the extra heat. In this instance, firing to get the coolest part of the kiln up to a minimum cone temperature is appropriate strategy even if it risks getting the middle of the kiln slightly hotter.
Downdraft Venting
A properly installed EnviroVent 2 downdraft vent system can also have a slight impact on heat uniformity in the kiln chamber when it is operating by drawing a small amount of heat toward the bottom of the kiln.
Cone Type and Placement
Skutt recommends using Orton self-supporting witness cones for the most accurate measurement of ceramic heat work. If large witness cones are used, they should be placed into Orton cone plaques rather than lumps of clay for more consistency. Junior kiln sitter cones are not designed to be used as witness cones.
Cones should be placed approximately 2 inches from the edge of the kiln shelf so that they are in a similar location to the heat being measured by the tip of the thermocouple. Cones placed in the middle of the kiln shelf will naturally be slightly cooler, especially in larger diameter kilns, because they are physically further away from the radiant heat of the elements and they may be shielded by pottery in the kiln. The variation will not be dramatic but it would be enough to show a difference in the cone bend. If a user is comfortable monitoring cones during a firing while wearing kiln glasses, the cones can be placed directly in front of the peep holes for viewing during the firing. If only one cone is used, it should be placed on the kiln shelf closest to the thermocouple. As a general practice for consistency, cones should routinely be placed in the same location in the kiln during each firing for better comparison over time.
Check out more helpful kiln articles on our blog.






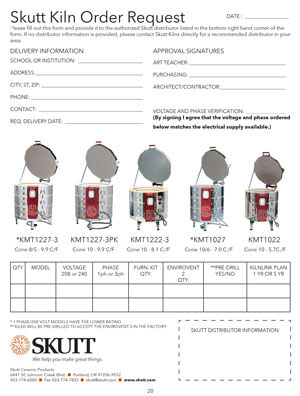



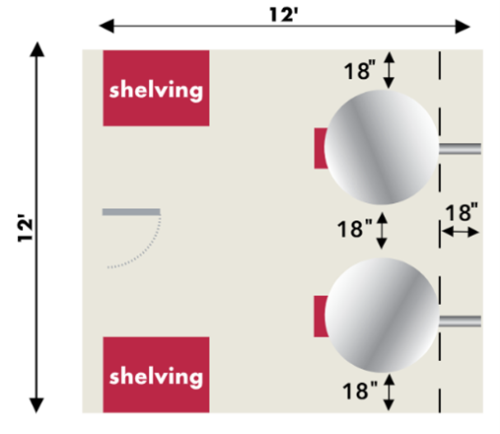







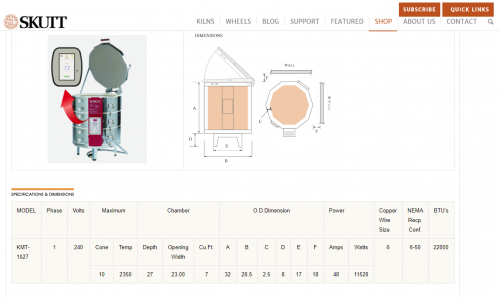
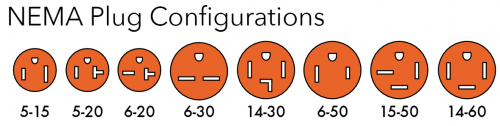 Staying with our KM-1027-3 example, the Build-A-Spec tool lists a NEMA 6-50 receptacle. This is the designation for what type of receptacle will match up with the plug on the end of the kiln’s power cord. NEMA is the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, and they have designations for every plug and matching receptacle organized by maximum amperage ratings. Skutt uses a limited number of plugs on the kilns we manufacture, but there are a variety of other plugs available for many other uses. It is advised to not alter the original plug on your kiln, and, in some cases, it could void your kiln warranty.
Staying with our KM-1027-3 example, the Build-A-Spec tool lists a NEMA 6-50 receptacle. This is the designation for what type of receptacle will match up with the plug on the end of the kiln’s power cord. NEMA is the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, and they have designations for every plug and matching receptacle organized by maximum amperage ratings. Skutt uses a limited number of plugs on the kilns we manufacture, but there are a variety of other plugs available for many other uses. It is advised to not alter the original plug on your kiln, and, in some cases, it could void your kiln warranty. 
 The best analogy for IR Compensation is the Cruise Control on your car. When you want to keep your car speed at a specific MPH you set your cruise control. When you come to a hill your car needs more power to climb the hill so your Cruise Control gives it the right amount of gas to keep the speed constant while climbing the hill.
The best analogy for IR Compensation is the Cruise Control on your car. When you want to keep your car speed at a specific MPH you set your cruise control. When you come to a hill your car needs more power to climb the hill so your Cruise Control gives it the right amount of gas to keep the speed constant while climbing the hill.
 These keys will display the temperature reading of the corresponding thermocouple on a Zone Control Kiln. Zone Control is an optional upgrade available that places a thermocouple in each section of the kiln. This allows the controller to sense when one section of the kiln is firing too hot or too cold and make adjustments during the firing.
These keys will display the temperature reading of the corresponding thermocouple on a Zone Control Kiln. Zone Control is an optional upgrade available that places a thermocouple in each section of the kiln. This allows the controller to sense when one section of the kiln is firing too hot or too cold and make adjustments during the firing.